Introduction: Experimental intestinal transplantation (ITx) in rats is a widely used tool in the study of ischemia reperfusion injury and rejection. Even so, live donors are used in the majority of these protocols. With the aim of generate a model closer to the clinical reality, our study intends to introduce brain death (BD) protocol to analyze the impact of biological processes associated with ITx.
Methods: Wistar rats between 280 - 330g were used, divided into two groups, Brain Death (BD n=5) and Non BD (n=3). Anesthetic induction was with isoflurane at 5%, maintenance was initially with a mask and then endotracheal 2/2.5% with AV (50 RPM - 2.5 TV). Arterial and venous lines are placed for blood pressure and fluid therapy manage. In the BD group, through a skull trepanation, a 4F balloon cannula is subdurally placed, and insufflated at 1ml/h flow rate. When Cushing reflex is observed, BD diagnosis is performed by the apnea test. The rat remains under BD for 2 hours, handling the MAP between 70 and 140 mmhg. NonBD group is ventilate assisted for 2 hours.
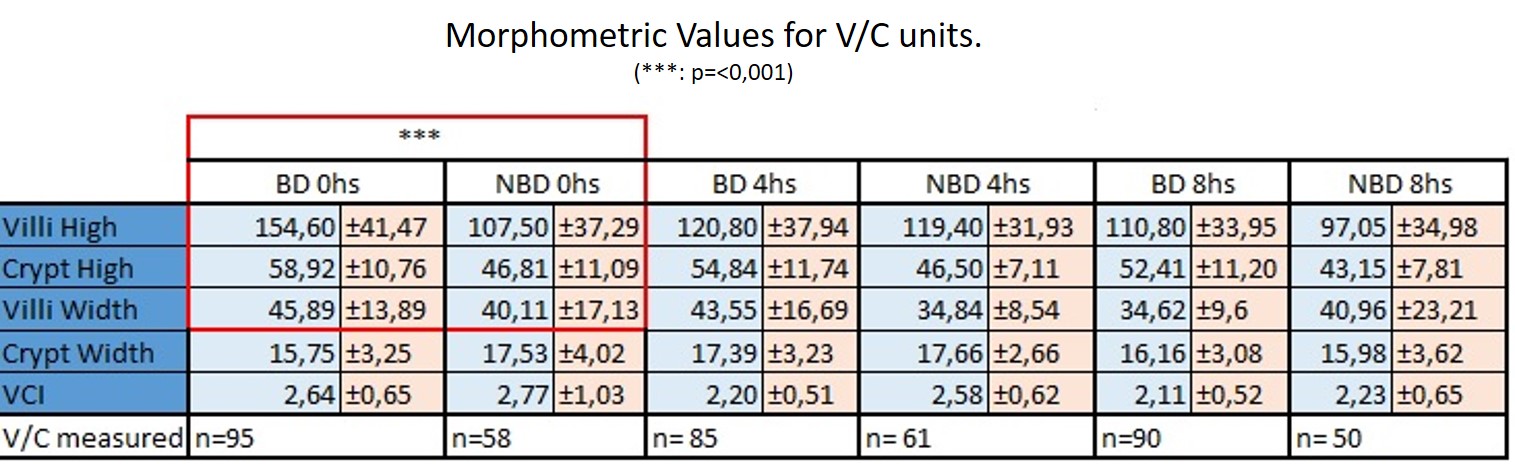
Afterwards, the graft is flushed with cold saline, harvested and preserved in HTK (Custodiol®) at 4°C. Then, sampled at 0, 4, 8, 12 and 24hs for H&E staining. For histological damage was used Park-Chiu scale. Using ImageJ® morphometric variables were measured. 207 V/C units in 5 individuals of BD group and 169 (3 individuals) for NonBD at 0, 4 and 8hs, Villi and Crypt height and width (VH, VW, CH and CW), with a minimum 10 and maximum 20 V/C units for each sample. In addition, the villus/crypt index (VCI) was calculated.
Results: A minor injury in the Non BD group was observed: 0hs NonBD=0.33 (±0.58) vs BD=0.8 (±0.84); 8hs NonBD= 2 (± 0) vs BD= 2.4 (±0.55); 12hs NonBD= 2.33 (±0.58) vs BD= 3 (±1.2).
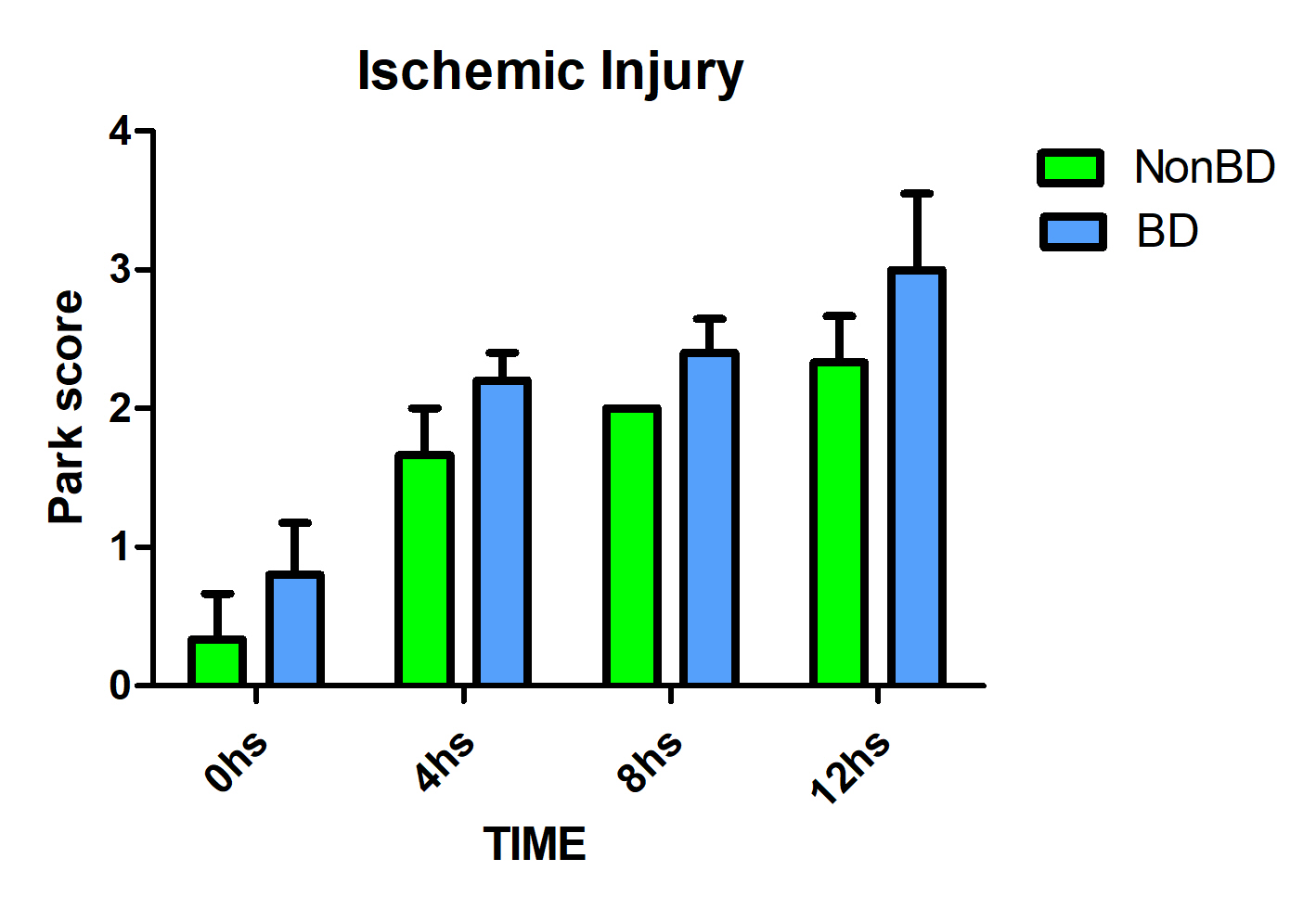
Higher scores of focal damage were reached faster in the BD group: BD= 4 (±1) at 8hs vs NonBD= 3.67 (±1.53) at 12hs.Morphometric values (μm) were higher under BD at 0hs for VH, VW and CH, (p=˂0.001). Decreasing VCI was observed in both groups at different times (BD: p= ˂0.001; NonBD: p=˂0.005).
Conclusions: We could establish a reliable BD model in rats for the study of its impact on the intestine transplantation graft. Our study shows that BD introduced subtle histopathological differences compared to ventilated controls. Future studies will be focused in the consequences of these changes analyzing the impact on graft function after the engraftment.
.jpg )