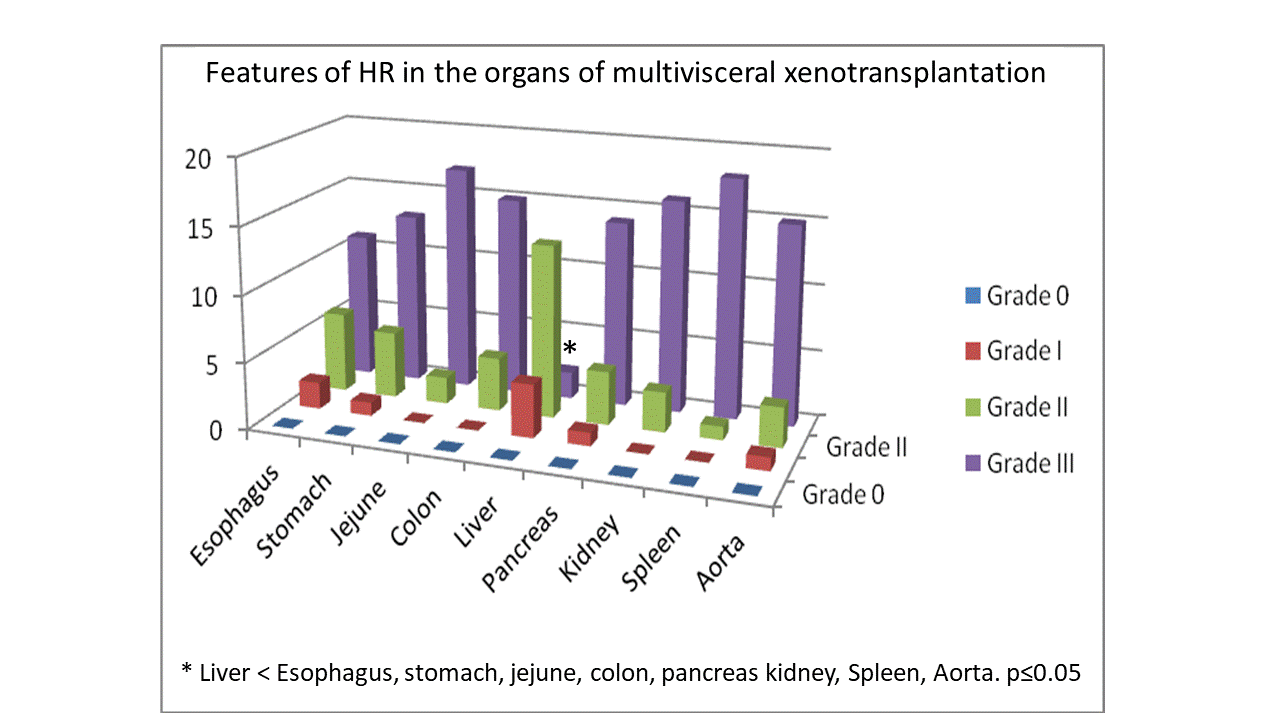
Xenotransplantation would be a solution for organs scarcity for transplantation however hyperacute rejection (HR) impair the this therapeutic method. We have described a model of discordant multivisceral xenotransplantation to assess the features of HR in various organs (1-3). Here we compare HR in the liver with the other organs of multivisceral xenograft. Method– After general anesthesia, multivisceral grafts containing esophagus, stomach, small intestine, colon, liver, pancreas, spleen and kidneys were recovery with a vascular pedicle containing the aorta with celiac axis and superior mesenteric artery and vena cava containing the hepatic veins were recovery from rabbits and implanted heterotopically in swine by aorta-aorta and cava-cava anastomosis (n=19). Multivisceral allotransplantation using rabbit-to-rabbit (n=5) composed the negative control group for HR. Three hours after graft reperfusion we sacrificed the animals and collected organs samples for histological study and IgG assessment by immunofluorescence. Features of HR were semi-quantitative graded in (0=normal, I=mild (edema, vascular congestion, and clumping of platelets in the microcirculation), II=moderate (diffuse edema, presence of some fibrin thrombi, intense vascular congestion, epithelial dysplasia, and foci of hemorrhage) and III=severe (presence of fibrin thrombi in all vessels, extensive interstitial edema, diffuse interstitial hemorrhage and confluent necrosis). T Student was used to compare HR in all organs from xenografts. Results – All animals were alive and well at the experimental end. The occurrence of HR was macroscopically noted in xenograft in 15 minutes. The autopsy revealed HR in all organs from multivisceral xenograft; however, we observed less severe HR in liver compared with esophagus, stomach, small intestine, colon, pancreas, spleen and kidneys (figure 1). IgG fixation was strong in in xenografts and absent in allografts. The occurrence of HR was absent in all allografts. Conclusion –Heterotopic discordant multivisceral xenotransplantation is a relevant tool to study HR. IgG fixation by immunofluorescence was strong in the sites of HR. Therefore, we show for the first time that the liver is more tolerant to HR after multivisceral xenotransplantation than the other abdominal organs.
References:
1.Galvão FH, et al. Xenotransplantation.2010;17(6):423-8.
2.Galvão FH, et al. Xenotransplantation.2008;15(3):184-90
3.Galvao FH, et al. Xenotransplantation.2012;19(5):298-304.
.jpg )