Introduction: Current guidelines on pediatric Parenteral Nutrition (PN) conclude that standardized PN mixtures are not suitable for children with chronic Intestinal Failure (IF) on home PN. However, studies evaluating efficacy or safety of standardized PN are lacking. Possible advantages of standardized PN could be a reduction in costs and a longer shelf life of PN. Therefore, this study was designed to assess the effects on growth and safety of standardized PN compared to individualized PN.
Methods: Retrospective cohort study in Dutch children on home PN between June 2017 and July 2018, in which Individualized PN was compared to standardized PN. Growth was assessed by calculating the difference of Weight-for-age (WFA), Height-for-age (HFA) and weight for height (WFH) SD scores between date of inclusion and 6, 12 and 24 months prior to inclusion. Primary outcome was growth over 2 years, secondary outcomes were electrolyte disturbances and biochemical abnormalities such as liver function. Non parametric tests were used to explore differences between groups.
Results: 50 patients (50% female, median age 6.5 years) were included, of whom 16 (32%) received standardized PN mixtures. Age (11 vs 5 years), gestational age (GA) (39.2 vs 36.2 weeks) and PN duration (97 vs 39 months) were significantly higher in the group receiving standardized PN (p: ≤.001; .027; .013 respectively). Type of underlying disease did not differ between groups. For children receiving standardized PN mixtures, median weight gain in 2 years was significantly higher compared to the individualized PN mixtures group of children where a mean SD score decrease was seen (+0.38 SD score vs -0.55 SD score, p: .003). No significant differences were demonstrated in HFA SD score change, WFH SD score change (Table 1), or electrolyte disturbances (Table 2) between groups. Median total bilirubin was 6.0 µmol/L (5.0 – 13.0) in the standardized PN group and 5.0 µmol/L (4.0 – 9.0) in the individualized PN group (p: .473).

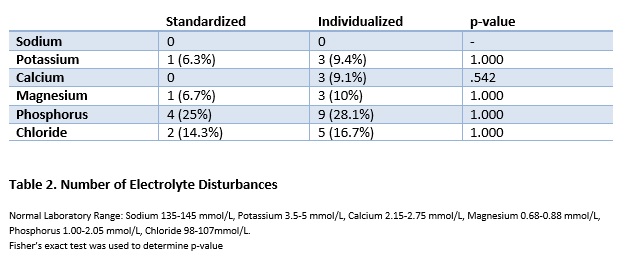
Conclusion: In children receiving standardized PN mixtures, change in WFA SD score was significantly higher compared to children receiving individualized PN. Standardized PN mixtures are at least non-inferior to individualized PN mixtures in terms of electrolyte disturbances and biochemical abnormalities in a home PN cohort. Therefore, standardized PN mixtures can safely be administered to patients with chronic IF if the composition of this mixture meets the nutritional need of the patient.
.jpg )