Purpose: Many different pre-conditioning immunosuppression protocols have been reported to improve outcomes of patient and graft survival in intestinal transplantation(IT). The use of Alemtuzumab as an immunosuppressant inducer is not well studied in pediatric IT. Our aim is to analyze its impact on immunological complications among this population, comparing different protocols used in our center.
M&M: A retrospective study of immunosuppresion protocols in pediatric(<18yrs) IT was conducted. 103 IT (55multivisceral, 25intestinal, 22hepatointestinal, 3modified multivisceral) were performed in 84patients (male predominance-60%-,mean age 5.3yrs) between Oct1999-Oct2018.
Mean time on the waiting list was 272days and waiting list mortality was25%. Main indications for the transplant on the first instance were short bowel sd.(69%), motility disorders(12%) and epithelial diseases(9.5%). The colon was included routinely from2012. Native spleen was preserved in 22/55(40%) of multivisceral grafts.
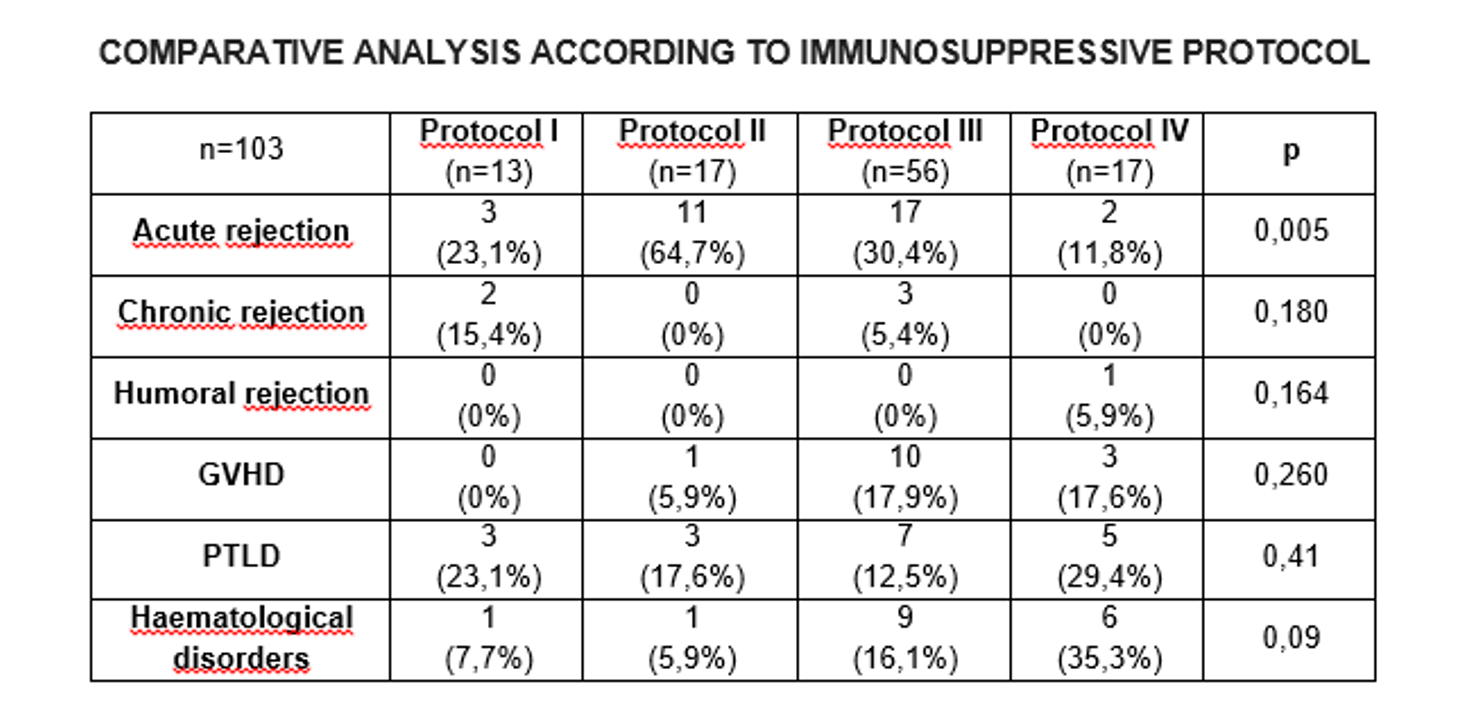
Immunossupression evolved over time in different stages, so we divided patients in 4 groups according to pre-conditioning regime (I-Basiliximab(n=13), II-Thymoglobulin(n=17), III-Basiliximab(n=56) and IV-Alemtuzumab(n=17)). Manteinance was performed in all cases with FK and steroids and also with Azathioprine in group I. Nowadays we use Alemtuzumab for patients >4yrs and retransplantation of any age and Basiliximab for the rest.
Results: Groups with highest and lowest acute rejection rates were group II(65%) and IV(12%) respectively(p<0.05). The latter presented the highest rates of PTLD(29%) and haematological disorders(35%). Despite this, it is the group with the lowest loss of grafts(45%).
Only 2cases of humoral rejection were observed in the whole series in group I and group IV, respectively. Regarding chronic rejection, 3cases in group I(23%) and 3cases in group III(5%) were observed. There were no cases of GVHD among patients in group I but 1case in group II(6%), 10in group III(18%) and 3in IV(18%) were registered.
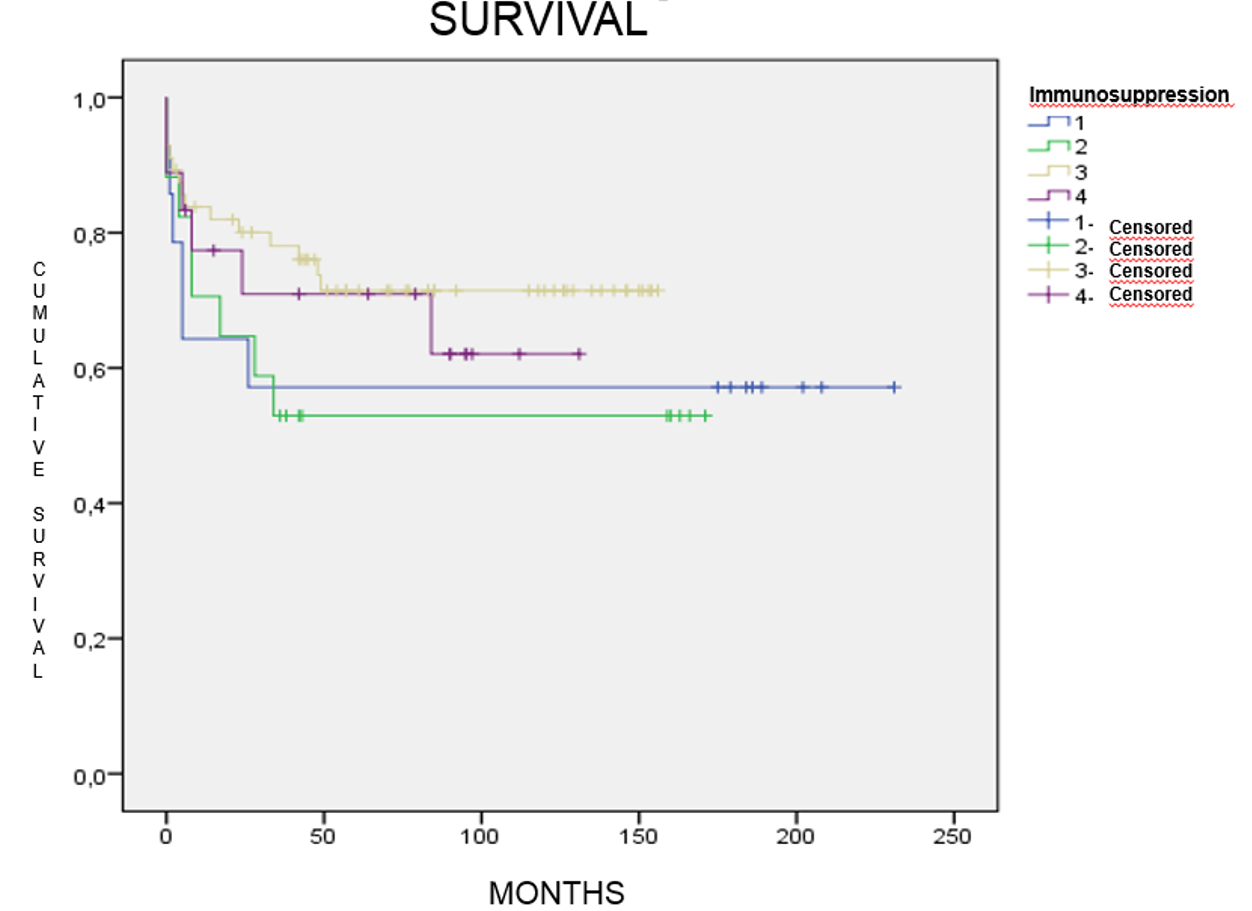
Finally, 35/84(42%) patients died during follow-up and survival percentages between 53%(group II) and 73%(group III) were recorded.
Conclusions: Alemtuzumab appears to be effective in pediatric IT patients with high immunological risk or retransplanted due to its low rates of acute and chronic rejection; however, further studies are needed to conclude its safety in pediatrics and the impact on PTLD, GVHD and hematological disorders compared to other therapies.
.jpg )